The Supply of Shipping Containers to the United States
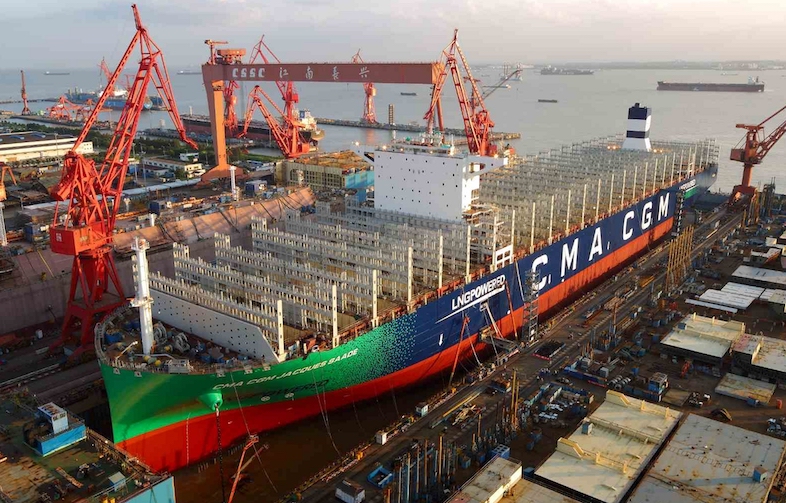
The global supply chain has been under immense strain over the past few years, and one of the most visible symbols of this turmoil is the humble shipping container. The current supply of these containers to the United States is a topic of considerable interest due to its impact on international trade, particularly with China, and the broader economic implications.
The State of Shipping Container Supply
As of 2023, the shipping container supply chain remains in a critical state. This situation has evolved from the imbalance that began in 2020 when North America experienced a 40% imbalance in container traffic – for every 100 containers that arrived, only 40 were exported.
While the container shortage was a significant issue during the height of the Covid pandemic, the global economy is currently facing the opposite problem: an oversupply of containers. This shift has resulted in a decrease in freight rates, with data showing a drop of more than 80% in the cost to ship a 40-ft container from Asia to the US West Coast since April 2022.
However, despite the oversupply, the distribution of containers remains a challenge. The Port of Los Angeles, the largest container port in the United States, handled nearly 10.7 million TEUs (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Units) in its 2022 fiscal year, illustrating the high volume of goods coming into the country.
 Trade Limitations Between China and the USA
Trade Limitations Between China and the USA
The trade relationship between the United States and China significantly impacts the supply of shipping containers. The ongoing trade war initiated during the Trump administration imposed tariffs on billions of dollars worth of goods, disrupting the flow of trade and consequently, the movement of shipping containers.
The imbalance in trade, with the US importing far more from China than it exports, exacerbates the container supply issue. Empty containers are often sent back to Asia, contributing to the oversupply in those regions while creating a deficit in the US.
Economic Implications
The supply of shipping containers is intrinsically linked to the health of the global economy. When there’s a disruption in the supply, it sends ripples across various sectors. Increased shipping costs due to container shortages can inflate the prices of imported goods, impacting consumer spending and potentially fueling inflation.
Moreover, the imbalance in container distribution also affects exporters who struggle to find containers for their goods, leading to delays and increased costs. This situation can hinder businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises, from accessing international markets, impacting economic growth.
Additionally, the congestion at ports due to the oversupply of containers can lead to delays in unloading goods, disrupting just-in-time supply chains, and causing shortages in various sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the current supply of shipping containers to the United States is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including trade policies and economic conditions. While the situation has improved from the severe container shortage experienced during the peak of the pandemic, challenges remain in terms of container distribution and port congestion. As the world continues to grapple with these issues, it’s clear that efficient and equitable solutions are needed to ensure the smooth functioning of the global supply chain.